Paediatric ankle fractures
Introduction
Acute trauma to the ankle can result in soft tissue or bony injury.
The physes are weaker than the adjacent bones and ligaments, making physeal fractures the most common ankle injury.
A wise adage to remember when
evaluating paediatric extremity injuries is that “children don’t get sprains”.
All growth plate fractures should be monitored closely for 2 years to observe for growth arrest. Partial growth arrest may result in angular deformity, requiring realignment osteotomy if missed. If noted early, physeal bar resection can be undertaken.
Note:
Several accessory ossification centres are normally seen at the tips of malleoli.
The distal tibial physis starts fusing medially and progresses laterally.
The fibula is last to fuse.
All major ligaments insert or originate in the distal tibial and fibular epiphysis
Classification
Dias and Tachdijan (paediatric version of Lauge Hansen) (1978)
Similar to Lauge Hansen, patterns based on position of foot and deforming force
-
Adolescent variants of Supination External Rotation
Juvenile Tillaux
Triplane fracture
Isolated distal fibular fractures
| Supination Inversion | Pronation Eversion External Rotation | Supination External Rotation | Supination Plantar Flexion | Axial Compression | Adolescent SER |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
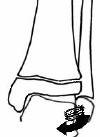
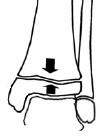
Supination - Inversion (SI)
Stage I - Avulsion of fibula physis (paediatric ankle sprain)
Stage II - Avulsion of Fibula physis and Salter Harris III or IV fracture of medial malleolus
Treatment (SI)
Stage I Treat as ankle sprain
Stage II Anatomical reduction of medial malleolus (closed or open). Hold with transepiphyseal screw
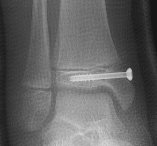
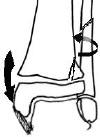
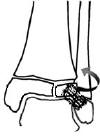
Pronation Eversion External Rotation (PEER)
Salter Harris II of distal tibia with lateral metaphyseal fragment
Greenstick metaphyseal-diaphyseal fibula fracture
Treatment (PEER)
Closed reduction and hold with transmetaphyseal screw
May fail to achieve closed reduction due to interposed tissue (periosteum)
Avoid valgus deformity beware of greenstick fibula
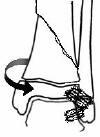
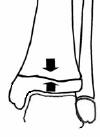
Supination External Rotation (SER)
Stage I - Salter Harris II fracture of distal tibia with postero lateral metaphyseal fragment (similar to SPF)
Stage II - Fracture tibia with spiral fracture fibular metaphysis
Treatment (SER)
Correct rotational deformity
Transmetaphyseal screw
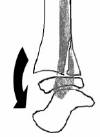
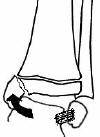
Supination Plantar flexion (SPF)
Salter Harris II fracture of distal tibia with pure posterior displacement and posterior metaphyseal fragment
Greenstick distal fibula fracture
Treatment (SPF)
Closed reduction
Anteroposterior metaphyseal screw
Reduction may be limited by interposed soft tissue or greenstick fibula fracture
Axial Compression
Salter Harris V compression injury
Rare injury may lead to growth arrest
Special adolescent fractures (Adolescent variant of SER)
So called transitional fractures
Occur due to asymetric fusion of distal tibial physis, begins to fuse posteromedial
(Click on links above for details on these injuries)
References
Dias LS, Tachdjian MO: Physeal injuries of the ankle in children: classification. Clin Orthop 1978, 136:230–233