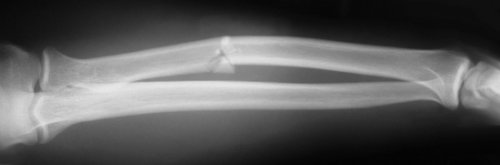
Forearm overview
AP and lateral in NEUTRAL rotation.
With pronation, the radius shortens affecting assesment of ulnar variance.
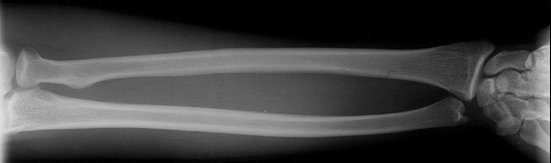
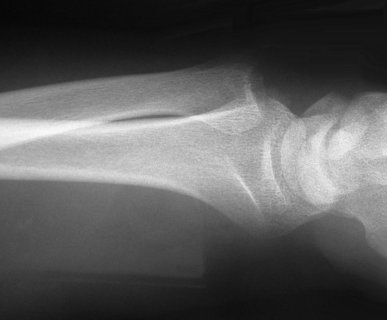
If you see a single bone fracture either radius or ulna look carefully at the Distal radio ulnar joint (DRUJ) and elbow. viz Galeazzi or Montegia injury
|
 |
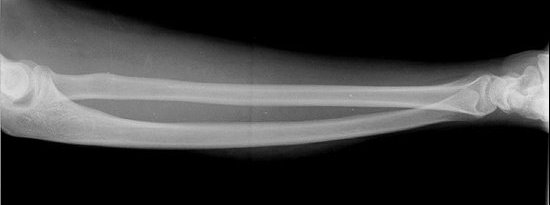
Radial Bow
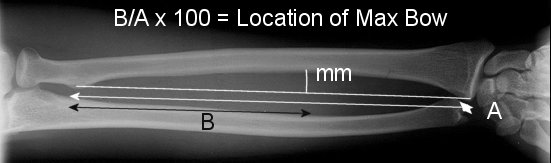 Schemitsch & Richards Schemitsch & Richards |
| A line is drawn from the bicipital tuberosity to the most ulnar aspect of the radius at the wrist. A perpendicular is drawn from the point of maximum radial bow to this line. The height of the perpendicular (defined as maximum radial bow) is measured in millimeters. The distance from the bicipital tuberosity to the previously measured perpendicular at the point of maximum radial bow is then measured and is recorded as a percentage of the length of the entire bow (the distance from the mid-point of the bicipital tuberosity to the most ulnar aspect of the subchondral bone of the distal aspect of the radius). This measurement is termed the "location of maximum radial bow". Radiographs of the contralateral forearm must be made in order to determine the variance from normal for individual patients. |