Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh
Anatomy:
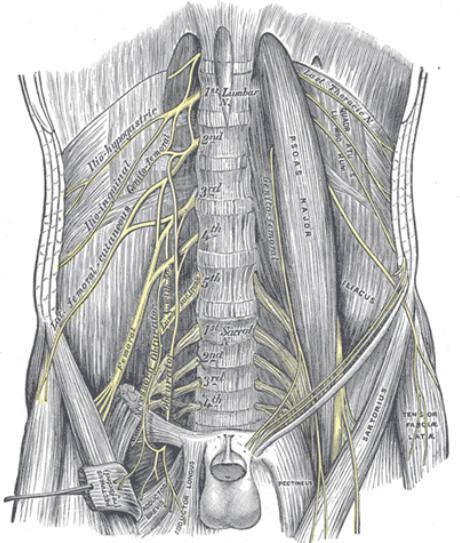
It is a branch of the lumbar plexus. It is formed in the substance of psoas
muscle from the dorsal divisions of second and third lumbar nerves. It
emerges from lateral end of the psoas muscle lying over the iliacus muscle
under the cover of iliac fascia. It runs obliquely across the iliac muscle
towards the anterior superior iliac spine. It passes underneath the inguinal
ligament and the pierces the lilac fascia to lie over the anterior surface of
the Sartorius muscle. It then lies between the Sartorius and tensor fascia
lata muscle sandwitched between fascia iliaca and fascia lata. Nerve is seen
to lie in a hammock formed by the iliac fascia as it passes over the Sartorius
and tensor fascia lata
How to locate the LFCN:
Indications:
1.Incision on the lateral side of
thigh: e.g. surgery for fracture neck of femur.
2.Skin graft from
lateral side of thigh
Contraindications: Absolute contraindications are
patient refusal and infection at the site of block.
Equipment:
1.Ultrasound machine with high frequency linear probe
2.Stimuplex or
equivalent 100 mm needle
3.Chlorhexidine 2% for asepsis
4.Local
anaesthetic: 5-10 ml of local anaesthetic (for analgesia 0.25% and
anaesthesia 0.5%)
Technique:
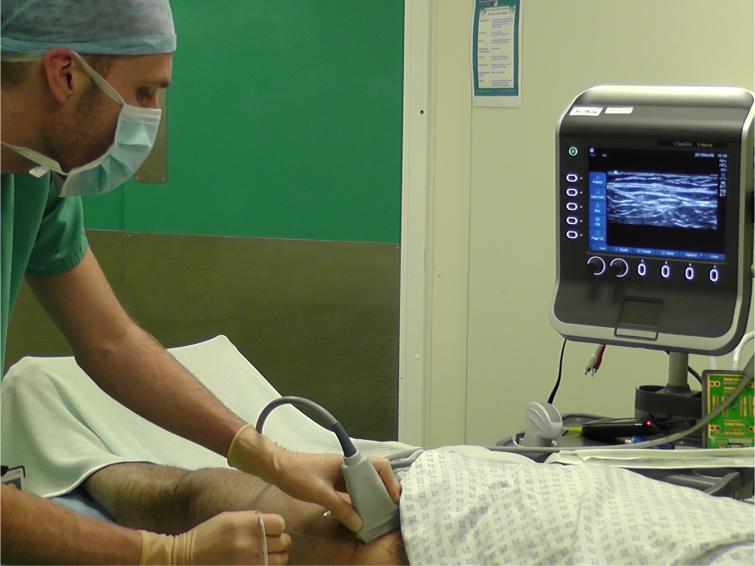
Patient lies supine. Anaesthetist stands on the
side of the patient the block is going to be done. The machine is positioned
as shown in the picture so that everything is easily visible and accessible to
the anaesthetist picture Ultrasound probe is placed below the inguinal crease
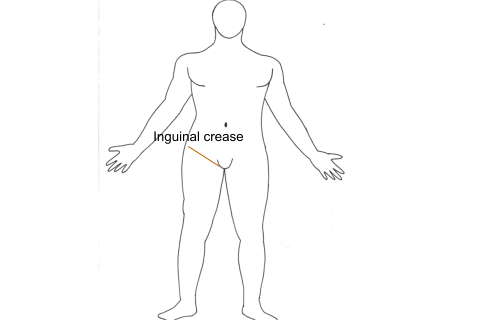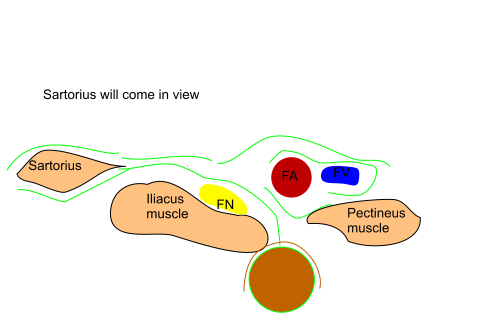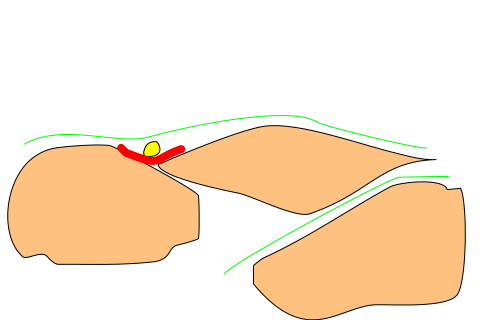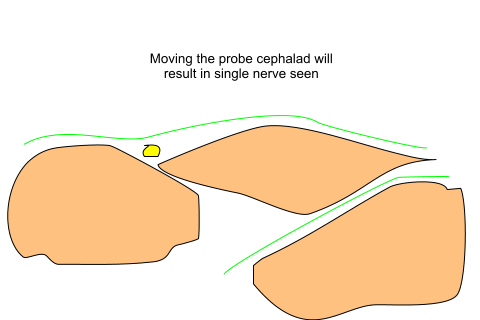
and parallel to it so that a cross sectional view of a single femoral artery
is obtained. Femoral artery,nerve and iliac fascia are identified. Sartorius
muscle is then identified. The probe is then centered over the Sartorius
muscle and turned in such a way that a good cross sectional view of the
Sartorius muscle is obtained. Probe is moved laterally so that the tensor
fascia lata is visulaised . Nerve will be then seen between as described
before. Needle is introduced in-plane so that the entire needle is visualized.
Local anaesthetic is then injected.



